Alternative Capital in (Re)insurance
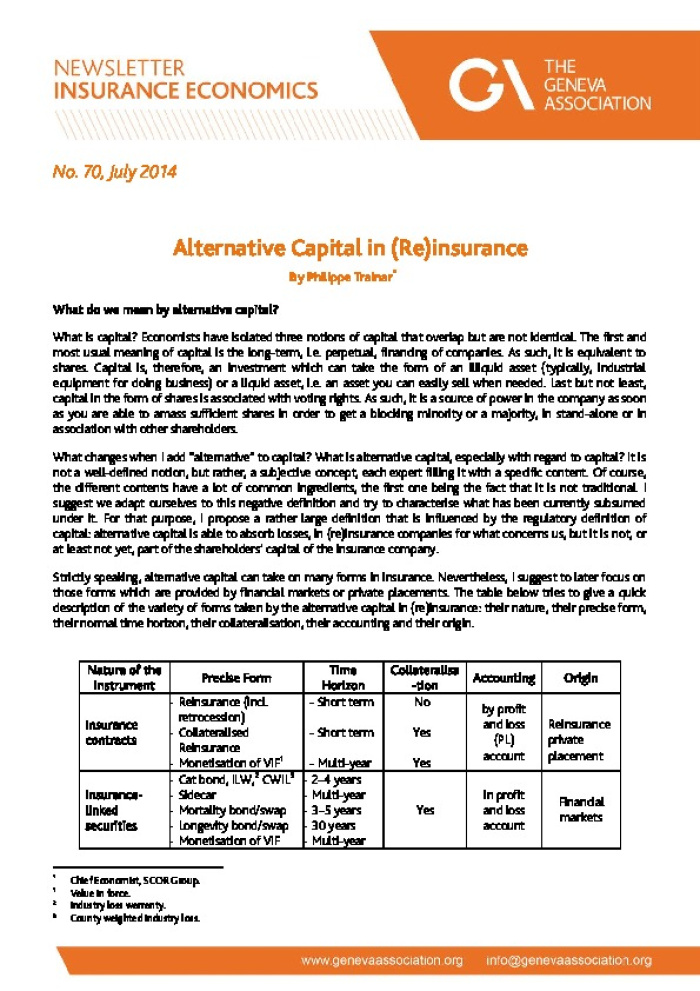
No. 70 , July 2014 Alternative Capital in (Re)insurance By Philippe Trainar* What do we mean by alternative capital? What is capital? Economists have isolated three notions of capital that overlap but are not identical. The first and most usual meaning of capital is the long -term, i.e. perpetual, financing of companies. As such, it is equivalent to shares. Capital is, therefore, an investment which can take the form of an illiquid asset (typically, industrial equipment for doing business) or a liquid asset, i.e. an asset you can easily sell when needed. Last but not least, capital in the form of shares is associa ted with voting rights. As such, it is a source of power in the company as soon as you are able to amass sufficient shares in order to get a blocking minority or a majority, in stand -alone or in association with other shareholders. What changes when I add ?alternative? to capital? What is alternative capital, especially with regard to capital? It is not a well -defined notion, but rather, a subjective concept, each expert filling it with a specific content. Of course, the different contents have a lot of co mmon ingredients, the first one being the fact that it is not traditional. I suggest we adapt ourselves to this negative definition and try to characterise what has been currently subsumed under it. For that purpose, I propose a rather large definition that is influenced by the regulatory definition of capital: alternative capital is able to absorb losses, in (re)insurance companies for what concerns us, but it is not, or at least not yet, part of the shareholders? capital of the insurance company. Strictly speaking, alternative capital can take on many forms in insurance. Nevertheless, I suggest to later focus on those forms which are provided by financial markets or private placements. The table below tries to give a quick description of the variety of forms taken by the alternative capital in (re)insurance: their nature, their precise form, their normal time horizon, their collateralisation, their accounting and their origin. Nature of the Instrument Precise Form Time Horizon Collateralisa -tion Accounting Origin Insurance contracts - Reinsurance (incl. retrocession) - Collateralised Reinsurance - Monetisation of VIF1 - Short term - Short term - Multi-year No Yes Yes by profit and loss (PL) account Reinsurance private placement Insurance- linked securities - Cat bond, ILW,2 CWIL3 - Sidecar - Mortality bond/swap - Longevity bond/swap - Monetisation of VIF - 2?4 years - Multi -year - 3 ?5 years - 30 years - Multi-year Yes in profit and loss account Financial markets * Chief Economist, SCOR Group . 1 Value in force. 2 Industry loss warranty. 3 County weighted industry loss .